前言 很高兴遇见你~
在本系列的上一篇文章中,我们介绍了关于 Android 字体的一些基础知识,还没有看过上一篇文章的朋友,建议先去阅读 Android字体系列 (一):Android字体基础 ,你会发现,我们设置的那三个属性最终都会去构建一个 Typeface 对象,今天我们就好好的来讲讲它
注意:本文所展示的系统源码都是基于Android-30 ,并提取核心部分进行分析
一、Typeface 介绍 Typeface 负责 Android 字体的加载以及对上层提供相关字体 API 的调用
如果你想要操作字体,无论是使用 Android 系统自带的字体,还是加载自己内置的 .ttf(TureType) 或者 .otf(OpenType) 格式的字体文件,你都需要使用到 Typeface 这个类。因此我们要全局修改字体,首先就要把 Typeface 给弄明白
二、Typeface 源码分析 源码分析环节可能比较枯燥,坚持就是胜利 ⛽️
1、Typeface 初始化 Typeface 这个类会在 Android 应用程序启动的过程中,通过反射的方式被加载。点击源码可以看到它里面有一个 static 代码块,它会随着类的加载而加载,并且只会加载一次,Typeface 就是通过这种方式来进行初始化的,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 static {final HashMap<String, Typeface> systemFontMap = new HashMap <>();if (sSystemFontMap.containsKey(DEFAULT_FAMILY)) {null , 0 );null , Typeface.BOLD);"sans-serif" , 0 );"serif" , 0 );"monospace" , 0 );new Typeface [] {null , Typeface.ITALIC),null , Typeface.BOLD_ITALIC),
上述代码写了详细的注释,我们可以发现,Typeface 初始化主要做了:
1、将系统的一些默认字体放入一个 Map 中
2、设置默认的字体
3、初始化一些默认字体
4、初始化一个 sDefaults 数组,存放一些常用的 Style
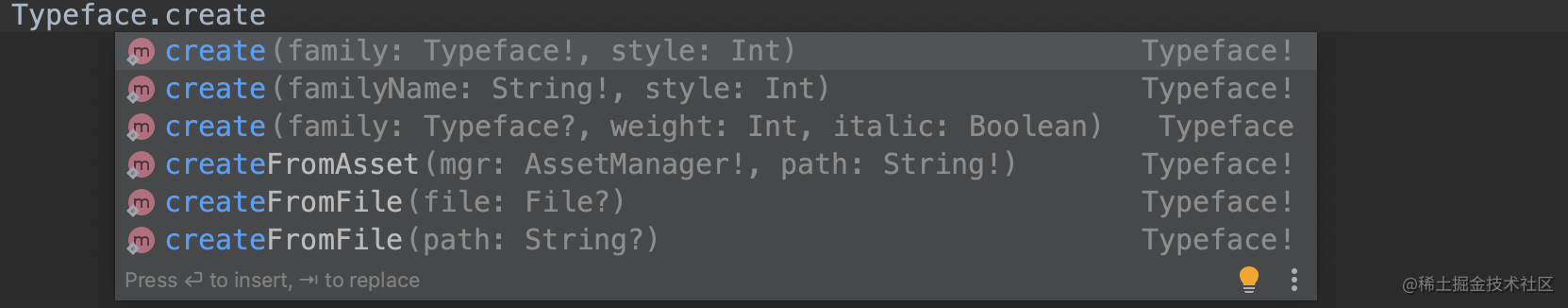
完成了 Typeface 的初始化,接下来看 Typeface 提供了一系列创建字体的 API ,其中对上层开放调用的有如下几个:
下面我们来重点分析这几个方法
2、通过 Typeface 和 Style 获取新的 Typeface 对应上面截图的第一个 API , 看下它的源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public static Typeface create (Typeface family, @Style int style) {if ((style & ~STYLE_MASK) != 0 ) {if (family == null ) {if (family.mStyle == style) {return family;final long ni = family.native_instance;synchronized (sStyledCacheLock) {if (styles == null ) {new SparseArray <Typeface>(4 );else {if (typeface != null ) {return typeface;new Typeface (nativeCreateFromTypeface(ni, style));return typeface;
从上述代码我们可以知道:
1、当你设置的 Typeface 和 Style 为 null 和 0 时,会给它们设置一个默认值
注意 :这里的 Style ,对应上一篇中讲的 android:textStyle 属性传递的值,用于设定字体的粗体、斜体等参数
2、如果当前设置的 Typeface 的 mStyle 属性和传入的 Style 相同,直接将 Typeface 给返回
3、从缓存中获取存放 Typeface 的容器,如果缓存中存在,则从容器中取出该 Typeface 并返回
4、如果不存在,则创建新的容器并加入缓存,然后通过 native 层创建 Typeface,并把当前 Typeface 放入到容器中
因此我们在使用的时候无需担心效率问题,它会把我们传入的字体进行一个缓存,后续都是从缓存中去拿的
3、通过字体名称和 Style 获取字体 对应上面截图的第二个 API:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public static Typeface create (String familyName, @Style int style) {return create(getSystemDefaultTypeface(familyName), style);private static Typeface getSystemDefaultTypeface (@NonNull String familyName) {Typeface tf = sSystemFontMap.get(familyName);return tf == null ? Typeface.DEFAULT : tf;
1、这个创建 Typeface 的 API 很简单,就是调用它的一个重载方法,我们已经分析过
2、getSystemDefaultTypeface 主要是通过 sSystemFontMap 获取字体,而这个 sSystemFontMap 在 Typeface 初始化的时候会存放系统提供的一些默认字体,因此这里直接取就可以了
4、通过 Typeface 、weight(粗体) 和 italic(斜体) 获取新的 Typeface 对应上面截图的第三个 API
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public static @NonNull Typeface create (@Nullable Typeface family, @IntRange(from = 1, to = 1000) int weight, boolean italic) {0 , 1000 , "weight" );if (family == null ) {return createWeightStyle(family, weight, italic);private static @NonNull Typeface createWeightStyle (@NonNull Typeface base, @IntRange(from = 1, to = 1000) int weight, boolean italic) {final int key = (weight << 1 ) | (italic ? 1 : 0 );synchronized (sWeightCacheLock) {if (innerCache == null ) {new SparseArray <>(4 );else {if (typeface != null ) {return typeface;new Typeface (return typeface;
通过上述代码可以知道,他与截图一 API 的源码很类似,无非就是将之前需要设置的 Style 换成了 weight 和 italic,里面的实现机制是类似的
5、通过 AssetManager 和对应字体路径获取字体 对应上面截图的第四个 API
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 public static Typeface createFromAsset (AssetManager mgr, String path) {Typeface typeface = new Builder (mgr, path).build();if (typeface != null ) return typeface;try (InputStream inputStream = mgr.open(path)) {catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException ("Font asset not found " + path);return Typeface.DEFAULT;public Builder (@NonNull AssetManager assetManager, @NonNull String path, boolean isAsset, int cookie) {new Font .Builder(assetManager, path, isAsset, cookie);public Typeface build () {if (mFontBuilder == null ) {return resolveFallbackTypeface();try {final Font font = mFontBuilder.build();final String key = mAssetManager == null ? null : createAssetUid(null ? DEFAULT_FAMILY : mFallbackFamilyName);if (key != null ) {synchronized (sDynamicCacheLock) {final Typeface typeface = sDynamicTypefaceCache.get(key);if (typeface != null ) {return typeface;final FontFamily family = new FontFamily .Builder(font).build();final int weight = mWeight == RESOLVE_BY_FONT_TABLEfinal int slant = mItalic == RESOLVE_BY_FONT_TABLEfinal CustomFallbackBuilder builder = new CustomFallbackBuilder (family)new FontStyle (weight, slant));if (mFallbackFamilyName != null ) {final Typeface typeface = builder.build();if (key != null ) {synchronized (sDynamicCacheLock) {return typeface;catch (IOException | IllegalArgumentException e) {return resolveFallbackTypeface();
上述代码步骤:
1、大量运用了 Builder 模式去构建相关对象
2、具体逻辑就是使用 createAssetUid 方法获取到当前字体的唯一 key ,通过这个唯一 key ,从缓存中获取已经被加载过的字体,如果没有,则创建一个 FontFamily 对象,经过一系列 Builder 模式,最终调用 native 层创建 Typeface 对象,并将这个 Typeface 对象加入缓存并返回
3、如果流程有任何异常,内部会调用 createWeightStyle 创建 Typeface 并返回
6、通过字体文件获取字体 对应上面截图的第五个 API
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public static Typeface createFromFile (@Nullable File file) {Typeface typeface = new Builder (file).build();if (typeface != null ) return typeface;if (!file.exists()) {throw new RuntimeException ("Font asset not found " + file.getAbsolutePath());return Typeface.DEFAULT;public Builder (@NonNull File path) {new Font .Builder(path);null ;null ;
从上述代码可以知道,这种方式主要也是通过 Builder 模式去构建 Typeface 对象,具体逻辑我们刚才已经分析过
7、通过字体路径获取字体 对应上面截图的第六个 API
1 2 3 4 public static Typeface createFromFile (@Nullable String path) {return createFromFile(new File (path));
这个就更简单了,主要就是创建文件对象然后调用另外一个重载方法
8、Typeface 相关 Native 方法 在 Typeface 中,所有最终操作到加载字体的部分,全部都是 native 的方法。而 native 方法就是以效率著称的,这里只需要保证不频繁的调用(Typeface 已经做好了缓存,不会频繁的调用),基本上也不会存在效率的问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 private static native long nativeCreateFromTypeface (long native_instance, int style) ;private static native long nativeCreateFromTypefaceWithExactStyle ( long native_instance, int weight, boolean italic) ;private static native long nativeCreateFromTypefaceWithVariation ( long native_instance, List<FontVariationAxis> axes) ;@UnsupportedAppUsage private static native long nativeCreateWeightAlias (long native_instance, int weight) ;@UnsupportedAppUsage private static native long nativeCreateFromArray (long [] familyArray, int weight, int italic) ;private static native int [] nativeGetSupportedAxes(long native_instance);@CriticalNative private static native void nativeSetDefault (long nativePtr) ;@CriticalNative private static native int nativeGetStyle (long nativePtr) ;@CriticalNative private static native int nativeGetWeight (long nativePtr) ;@CriticalNative private static native long nativeGetReleaseFunc () ;private static native void nativeRegisterGenericFamily (String str, long nativePtr) ;
到这里,关于 Typeface 源码部分我们就介绍完了,下面看下它的一些其他细节
三、Typeface 其它细节 1、默认使用 在初始化那部分,Typeface 对字体和 Style 有一些默认实现
如果我们只想用系统默认的字体,直接拿上面的常量用就 ok 了,如:
1 2 3 4 5 Typeface.DEFAULT
而如果想要设置 Style ,我们不能通过 sDefaults 直接去拿,因为上层调用不到 sDefaults,但是可以通过 Typeface 提供的 API 获取:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public static Typeface defaultFromStyle (@Style int style) {return sDefaults[style];
2、Typeface 中的 Style 1)、Typeface 中的 Style 可以通过 android:textStyle 属性去设置粗体、斜体等样式
2)、在 Typeface 中,这些样式也对应了一个个的常量,并且 Typeface 也提供了对应的 Api,让我们获取到当前字体的样式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public static final int NORMAL = 0 ;public static final int BOLD = 1 ;public static final int ITALIC = 2 ;public static final int BOLD_ITALIC = 3 ;public @Style int getStyle () {return mStyle;public final boolean isBold () {return (mStyle & BOLD) != 0 ;public final boolean isItalic () {return (mStyle & ITALIC) != 0 ;
3、FontFamily 介绍 FontFamily 主要就是用来构建 Typeface 的一个类,注意和在 Xml 属性中设置的 android:fontFamily 区分开来就好了
四、总结 总结下本篇文章所讲的一些重点内容:
1、Typeface 初始化对字体和 Style 会有一些默认实现
2、Typeface create 系列方法支持从系统默认字体、 assets 目录、字体文件以及字体路径去获取字体
3、Typeface 本身支持缓存,我们在使用的时候无需注意效率问题
好了,本篇文章到这里就结束了,希望能给你带来帮助 🤝
感谢你阅读这篇文章
下篇预告 下篇文章我会讲在 Xml 中使用字体,敬请期待吧 😄
参考和推荐 Android 修改字体,跳不过的 Typeface
你的点赞,评论,是对我巨大的鼓励!
欢迎关注我的公众号: sweetying
如果有问题 ,公众号内有加我微信的入口,在技术学习、个人成长的道路上,我们一起前进!